
Why HUGMYFEET™ Compression & Diabetic Socks Make the Perfect Christmas Gift
When Christmas rolls around, we all hit that same problem: “What do I buy that’s actually useful, thoughtful, and not just more clutter?” If you’ve got someone in your life...

How to Wash & Store Your HUGMYFEET™ Compression & Diabetic Socks
When you finally find socks that actually feel good – soft, non-restrictive, and supportive – the last thing you want is for them to lose their shape after a few washes. That’s...

Why Compression Socks Are a Must-Have This Winter and the Perfect Gift for Cozy Feet!
HUGMYFEET™ compression socks boost circulation, keep legs warm and add style non-binding, diabetic-friendly. Festive season ready in black or funky prints.

Compression Socks For Swelling
Understanding Swelling in the Lower Legs Swelling, or edema, in the feet, ankles, and lower legs is a frequent complaint, especially among individuals who stand or sit for prolonged periods,...

What Are Diabetic Socks and Why Do They Matter?
Living with diabetes requires daily attention, from monitoring blood sugar to making lifestyle adjustments that protect long-term health. Among these small yet powerful adjustments is a choice many people overlook—diabetic...

Compression Socks for Neuropathy: What Science and Medicine Reveal
Neuropathy, particularly peripheral neuropathy, is one of the most common complications of diabetes and other chronic conditions. It occurs when nerve damage disrupts communication between the brain, spinal cord, and...
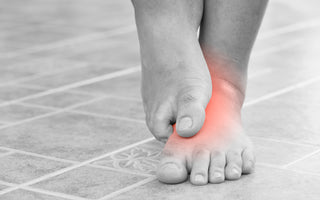
Neuropathy in the Feet: Causes, Aggravating Factors, and Treatments
Neuropathy in the feet, also known as peripheral neuropathy, is a common yet often underestimated health issue. It occurs when the peripheral nerves, those outside the brain and spinal cord, are...

Understanding A1C: What It Is, Why It Matters, and How It Relates to Diabetes
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose (sugar) levels, caused either by insufficient insulin production (Type 1 diabetes), by insulin resistance (Type 2), or by other factors...
